The tasks [edit] 1. NAT solves the problem of a limited range of IP addresses, it is significant until the final transition to IPV6 occurs. 2. allows you to limit communication
Tasks [edit]
1. NAT solves the problem of a limited range of IP addresses, it is significant until the final transition to IPV6 occurs.
2. It allows you to limit communication from the outside to the inner hosts, while the ability to communicate from the inside remains.
3. It makes it possible to hide the internal services of internal hosts/servers. You can replace the internal port of the officially registered service (for example, the 80th port of the TCP (HTTP server) on the external 54055). Thus, outside it will be possible to get to the site at the address http://example.org:54055, but on the internal server located behind NAT, the work of the http server will occur at the usual 80th port, that is, the 80th port The server will not be available from the Internet for a direct incoming connection.
The principle of work [edit]
The computer can be connected to the Internet directly (white IP address, usually when connecting directly to the modem), or via NAT-then the computer has a local IP address, inaccessible (private, gray) from the Internet. Gray addresses include addresses from the following ranges:
| Range | The number of hosts |
|---|---|
| 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255/8 | 16 777 216 hosts |
| 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255/12 | 1 048 576 hosts |
| 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255/16 | 65 536 hosts |
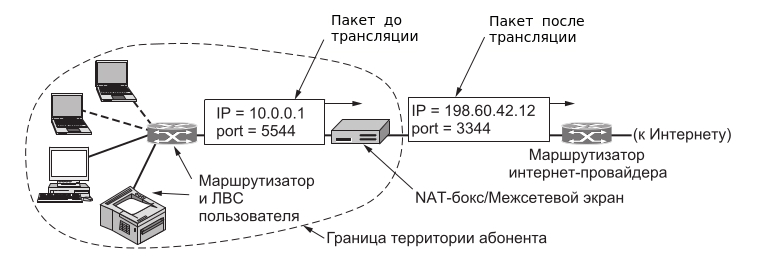
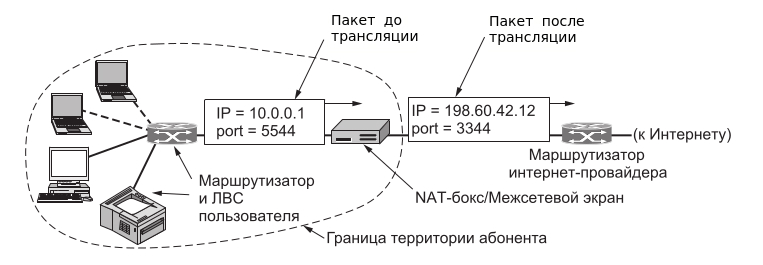
The address is converted by the NAT method can be carried out by almost any routing device – a router, access server, inter -member screen. Taking a package from a local computer, the router looks at the IP address. If this is a local address, then the package is sent to another local computer. If not, then the package must be sent out to the Internet. But after all, the return address in the package indicates the local address of the computer, which will be unavailable from the Internet. Therefore, the router “on the fly” broadcasts (replaces) the reverse IP address of the package on its external (visible from the Internet) IP address and changes the port number (to distinguish between retaliatory packages addressed to different local computers). The combination necessary for the reverse substitution, the router saves in his temporary table. Some time after the client and the server are finished exchanging packages, the router will bother in his table a record of the N-th port for the statute of limitations.
Example [edit]
Types NAT [edit]
Static [edit]
One internal address is converted into one external, all requests that come to the external address will be broadcast to the internal one, as if the host is the owner of a white IP address. This approach is useful when there is a server inside a private network, which requires full access from the outside. The minus of the approach is that it does not help save white addresses.
Dynamic [edit]
There is a pool of white addresses, for example, the provider allocated the network 198.51.100.0/28 with the 16th addresses. Two of them (the first and last) – the address of the network and broadcasting, two more addresses are assigned to equipment for ensuring routing.NAT_VIKIKONSPEKTI
NAT – Wikisconkems
The tasks [edit] 1. NAT solves the problem of a limited range of IP addresses, it is significant until the final transition to IPV6 occurs. 2. allows you to limit communication
Tasks [edit]
1. NAT solves the problem of a limited range of IP addresses, it is significant until the final transition to IPV6 occurs.
- 2. It allows you to limit communication from the outside to the inner hosts, while the ability to communicate from the inside remains.
- 3. It makes it possible to hide the internal services of internal hosts/servers. You can replace the internal port of the officially registered service (for example, the 80th port of the TCP (HTTP server) on the external 54055). Thus, outside it will be possible to get to the site at the address http://example.org:54055, but on the internal server located behind NAT, the work of the http server will occur at the usual 80th port, that is, the 80th port The server will not be available from the Internet for a direct incoming connection.
- The principle of work [edit]
- The computer can be connected to the Internet directly (white IP address, usually when connecting directly to the modem), or via NAT-then the computer has a local IP address, inaccessible (private, gray) from the Internet. Gray addresses include addresses from the following ranges:
- Range
The number of hosts
16 777 216 hosts1 048 576 hosts
65 536 hostsThe address is converted by the NAT method can be carried out by almost any routing device – a router, access server, inter -member screen. Taking a package from a local computer, the router looks at the IP address. If this is a local address, then the package is sent to another local computer. If not, then the package must be sent out to the Internet. But after all, the return address in the package indicates the local address of the computer, which will be unavailable from the Internet. Therefore, the router “on the fly” broadcasts (replaces) the reverse IP address of the package on its external (visible from the Internet) IP address and changes the port number (to distinguish between retaliatory packages addressed to different local computers). The combination necessary for the reverse substitution, the router saves in his temporary table. Some time after the client and the server are finished exchanging packages, the router will bother in his table a record of the N-th port for the statute of limitations.
Example [edit]
Types NAT [edit]
Static [edit]
One internal address is converted into one external, all requests that come to the external address will be broadcast to the internal one, as if the host is the owner of a white IP address. This approach is useful when there is a server inside a private network, which requires full access from the outside. The minus of the approach is that it does not help save white addresses.
- Dynamic [edit]
- There is a pool of white addresses, for example, the provider allocated the network 198.51.100.0/28 with the 16th addresses. Two of them (the first and last) – the address of the network and broadcasting, two more addresses are assigned to equipment for ensuring routing.The twelve remaining addresses can be used for NAT and release your users through them.
- The situation is similar to static NAT – one private address is translated to one external one – but now the external one is not clearly fixed, but will be selected dynamically from the specified range. The problem of the approach is the same as in the case of static NAT – the problem of limited white addresses is not solved.
Many-to-One[edit]
The next type has several names: NAT Overload, Port Address Translation (PAT), IP Masquerading, Many-to-One NAT. The essence of this type is that many private ones come out through one external address. This approach, unlike the previous ones, allows you to solve the problem with the lack of external addresses.
NAT problems[edit]
The principle of network addresses does not fit into the IP architecture, which implies that each IP address uniquely identifies only one machine in the world.
- NAT violates the end-to-end principle that every host must be able to send a packet to every other host at any given time. Since NAT address mapping is determined by outgoing packets, incoming packets are not received until outgoing packets have been sent.
- NAT transforms the Internet from a connectionless network to something like a connection oriented network. The problem is that the NAT block must maintain a mapping table for all connections passing through it. Remembering connection state is a matter of connection-oriented networks, not connectionless networks.
- Using NAT violates one of the fundamental rules of building layered protocols: the [math]k[/math] layer must not make any assumptions about what exactly the [math]k + 1[/math] layer has placed in the payload field.
- Processes on the Internet are not required to use only TCP or UDP. If the user of machine [math]A[/math] decides to come up with a new transport layer protocol to communicate with the user of machine [math]B[/math] , then he will have to somehow deal with the fact that NAT cannot correctly process the Source Port field TCP.
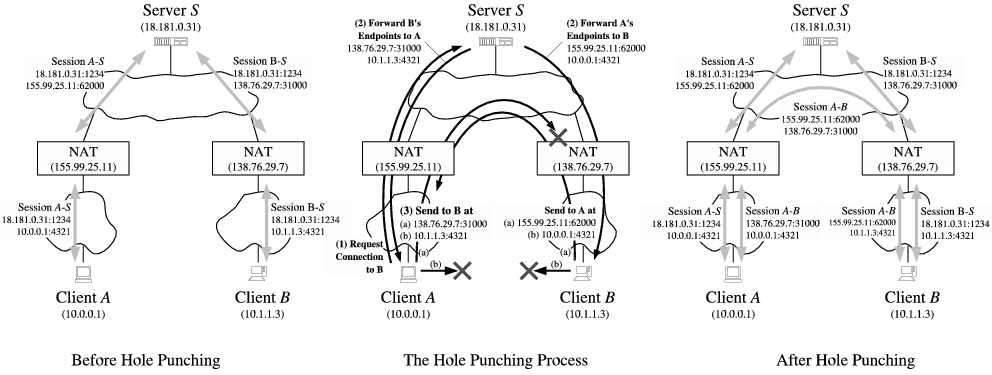
Hole Punching [edit]