In some patients who recovered from COVID-19, doctors noted a weakening of lung function. But there is good news: the likelihood of re-infecting the virus is extremely small.
Can coronavirus lead to long-term health problems?
In some patients who recovered from COVID-19, doctors noted a weakening of lung function. But there is good news: the likelihood of re-infecting the virus is extremely small.
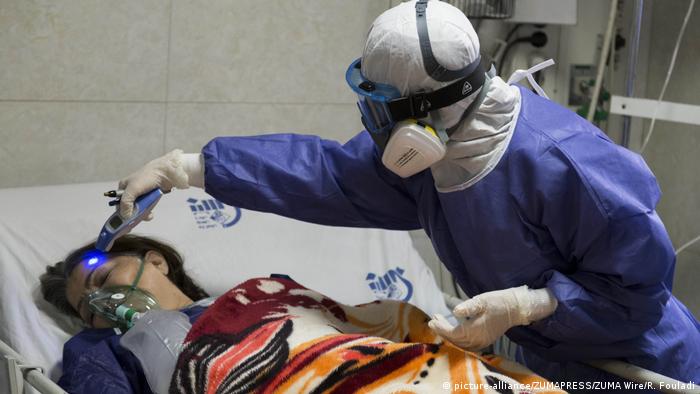
A woman with coronavirus being examined in a hospital in Tehran
The statistics are encouraging: as of Tuesday, March 24, more than 100,000 COVID-19 cases worldwide have already recovered. Most of these people had a mild or moderate disease, and in more serious cases, patients were provided with qualified medical care.
The recovered describe with relief how they managed to get through this difficult period – the treatment of symptoms, the horrific uncertainty and the grueling quarantine. They rejoice that having been ill with the coronavirus, they have developed immunity to this disease. However, there is no complete information about how people feel after recovery.
Possible consequences of COVID-19 – decreased lung function and shortness of breath
In the coming months, it will become clear whether the coronavirus infection can lead to long-term health consequences. SARS-CoV-2 is an infectious agent that primarily infects the lower respiratory tract, so people who carry the virus in moderate to severe form mostly suffer from dry cough, choking or pneumonia.
At the same time, it is possible that health problems may persist after recovery. Chinese doctors stated that individual patients who recovered from COVID-19 had weakened lung function and persistent shortness of breath. Some recovered patients may experience a decrease in lung function by 20-30 percent. They suffocate when they walk fast, said Owen Zeng, head of the infectious diseases center at Princess Margaret Hospital in Hong Kong.
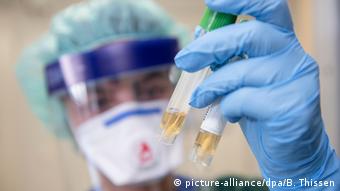
Some COVID-19 survivors experience changes in lung function
In a number of patients, during computed tomography, darkening was found in the lungs, which may indicate damage to them. Previously, similar effects of the disease were observed during research in Wuhan in early February. In one study conducted at the Wuhan University Hospital, 140 images of the lungs of patients were analyzed and blackout was detected in all cases.
Suspicion of pulmonary fibrosis
However, it is too early to draw comprehensive conclusions: at the moment, too little data has been analyzed. Further research should show whether coronavirus infection contributes to the development of pulmonary fibrosis, a pathological process in which connective tissue grows in the walls of the alveoli (lung vesicles).
Because of this, the patient experiences a chronic lack of oxygen, he develops rapid breathing, shortness of breath and dry reflex cough. This negatively affects, among other things, the working capacity of a person: it becomes difficult for him to perform even simple daily activities.
Pulmonary fibrosis is not treated because lung tissues that have undergone changes are no longer restored. However, with a timely diagnosis, the development of the disease can be slowed down or even stopped.
Is immunity to coronavirus developed??
Most experts are convinced that people who recover from COVID-19 develop immunity to this disease. This applies equally to those who have had a mild illness, with little or no symptoms. The human immune system even in this case reacts to the virus and produces the appropriate antibodies. Therefore, re-infection with coronavirus in people who have already had it is extremely unlikely.

How the world is fighting the coronavirus
More than 188 countries are affected by the coronavirus pandemic
The total number of people infected with coronavirus in the world by June 12, according to Johns Hopkins University, was about 7.5 million people, the epidemic covered at least 188 countries and territories. About 3.5 million people have recovered, more than 420 thousand have died from the consequences of coronavirus infection.

How the world is fighting the coronavirus
Events canceled around the world
Due to the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, public events, especially sports, are being canceled around the world. The Olympic Games in Tokyo were postponed a year later, in Germany the world's largest tourism fair ITB in Berlin, the Leipzig Book Fair, the Craft Fair in Munich, as well as the annual Oktoberfest beer festival were canceled (pictured).

How the world is fighting the coronavirus
Europe is trying to protect itself from the coronavirus
Fearing the rapid spread of the coronavirus, almost all EU countries closed their national borders. Classes in educational institutions were at first completely canceled, later they were restored to a very limited extent. Pictured: A medical worker at the Austrian-Italian border measures the temperature of a car driver. An elevated temperature is a reason for a ban on entry into the country.

How the world is fighting the coronavirus
Italy, Spain, UK
Italy and Spain were the first in Europe to be hit hardest by the coronavirus. In Italy, quarantine throughout the country has been introduced since March 9. The streets and squares of Italian cities were empty, and the army was involved in maintaining public order (see photo). By the end of May, the maximum number of deaths from SARS-CoV-2 in Europe was recorded in the UK.

How the world is fighting the coronavirus
Germany: gradual easing of quarantine measures
Until February 25, only 16 cases of coronavirus infection were registered in Germany. But then the number began to rise sharply.By June 12, the number of infected exceeded 186 thousand people. Most of all the infection is in the lands of Bavaria, the North Rhine – Westphalia and Baden -Württemberg. About 8.7 thousand people died. Since April 27, a gradual mitigation of quarantine measures has begun in the country.

How the world fights coronavirus
Azhiotazy demand for disinfectants
Due to the outbreak of coronavirus in Germany, there was a stir for disinfectants and liquid soap. In supermarkets and household chemical stores, shelves were initially empty, previously clogged with all kinds of bottles and tubes with antiseptics. By May, the supply was restored. In some stores, there are only announcements with a request not to buy goods to create reserves at home.

How the world fights coronavirus
Coronavirus reached Russia
The number of coronavirus in Russia by June 12 exceeded 510 thousand people. The largest number of cases is registered in Moscow, the Moscow Region, St. Petersburg and the Nizhny Novgorod region. Since April 15, a universal checkpoint has been in force in Moscow and MO. The platform for the issuance of such digital passes is planned to be introduced in the 21st region of Russia.

How the world fights coronavirus
Israel: hard quarantine brought the results
In Israel by June 12, coronavirus was diagnosed in more than 18 thousand people. Hard measures were taken in the country to combat the spread of coronavirus including full quarantine and a ban on entering the country of foreigners. On April 19, a gradual mitigation of quarantine measures began, separate non -food stores opened and the movement of public transport resumed.

How the world fights coronavirus
Iran: real numbers can be much worse than official
By June 12, more than 180 thousand sick and more than 8.5 thousand deaths were registered in Iran. However, it is possible that in reality the numbers can be much higher. Trying to prevent the spread of the virus, the Iranian authorities instructed to abundantly fill the streets of cities with disinfectants (in the photo).

How the world fights coronavirus
China: Coronavirus Epidemic went on decline
Meanwhile, in China, where at the end of 2019 a flash of SARS-COV-2 began, there are no new cases of infection. Most hospitals built for coronavirus in Jun are closed. In the photograph there are doctors of one of the temporary hospitals in Juan at the closing ceremony. In total, about 84 thousand people fell ill in China with a coronavirus infection, about 4600 died.
How the world fights coronavirus
Who is most susceptible to coronavirus infection?
The most dangerous coronavirus infection for the elderly older than 80 years and people with chronic cardiovascular, respiratory diseases, diabetes and hypertension. It is in these groups that the maximum risk of death. Another risk group is medical workers. In most patients – about 80 percent – the disease takes place in a mild or relatively mild shape.

How the world fights coronavirus
When will the vaccine appear from coronavirus?
The number of laboratories working on the creation of a vaccine against coronavirus SARS-COV-2 around the world cannot be counted. Scientists have already created several options for vaccines and test them on animals. In the USA and the UK, tests are also carried out in public. But with the most favorable course of events, the vaccine may appear on the market no earlier than mid -2021.