In CDC 24, a full-fledged check of bones is carried out – densitometry. We have the necessary settings for a high-quality, complete analysis of the condition of your bones.
DENSITOMETRY
Bone densitometry is used to measure bone content and density. This measurement may indicate decreased bone mass, a condition in which bones are more fragile and more prone to breaking or breaking. Bone densitometry is used primarily to diagnose osteoporosis and determine the risk of fractures. The testing procedure measures the bone density of the spine, pelvis, shoulders, and hips.
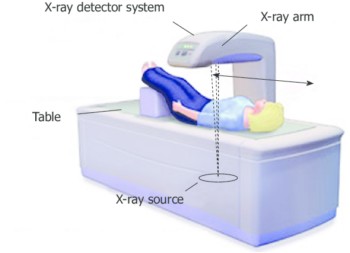
Bone densitometry testing can be done using x-rays, dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA), or by quantitative CT scanning using specific bone density software for the hip or spine. These procedures are usually performed in a clinic, hospital, or a stand-alone radiology unit, such as CDC 24.
However, for mass screening, there are portable types of bone densitometry testing. Portable testing is performed using a DEXA (or DXA) x-ray device or a quantitative ultrasound unit. Both types of hand tests may use the radius (one of the two bones of the lower hand), wrist, fingers, or heel to be tested. Portable testing, while useful for general screening, is not as accurate as non-portable methods because only one part of the bone is tested.
Standard x-rays can detect weakened bones. However, while bone weakness is evident on standard x-rays, bone weakness may be too advanced for treatment to be effective. A bone densitometry test can detect a decrease in bone density and strength at a much earlier stage, when treatment for bone weakness can be beneficial and effective.
Osteoporosis affects more than 10 million people – one in two women and one in four men. Fortunately, it can be prevented and easily detected with a bone density test (or DXA scan). Once osteoporosis is diagnosed, it can be treated before it causes a broken bone.
What does densitometry testing say?
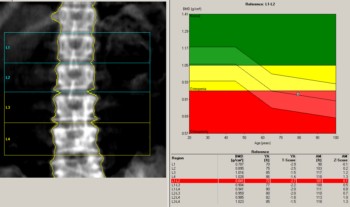
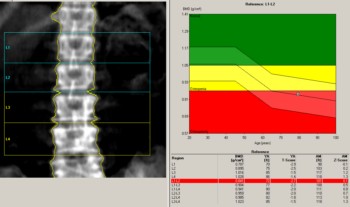
A bone densitometry test measures bone mineral density (BMD). Your BMD is compared to two norms – healthy young adults (your T-score) and age-matched (your Z-score).
First, your BMD score is compared to BMD scores in healthy adults aged 25 to 35 of your gender and ethnicity. The standard deviation (SD) is the difference between your BMD and the standard health of healthy young people. This result is your T-score.Positive T-scores indicate that the bone is stronger than normal; negative T-scores indicate that the bone is weaker than usual.
According to the World Health Organization, osteoporosis is defined based on the following levels of bone density:
- T-score within 1 SD (+1 or -1) of the average adult indicates normal bone density
- A T-score of 1 to 2.5 SD below the adult mean (-1 to -2.5 SD) indicates low bone mass.
- A T-score of 2.5 SD or more below the adult average (greater than -2.5 SD) indicates the presence of osteoporosis.
In general, the risk of bone fracture doubles for every SD below normal. Thus, a person with a BMD of 1 SD below normal (T-score -1) has twice the risk of a bone fracture as a person with a normal BMD. A person with a T-score of -2 has a four times greater risk of a bone fracture than a person with a normal BMD. Once this information is known, people at high risk of bone fracture can be treated to prevent future fractures. Severe (established) osteoporosis is defined as having a bone density that is greater than 2.5 SD below the average adult with one or more previous fractures due to osteoporosis.
Secondly, your BMD is compared to the age norm. This is called your Z-score. Z-scores are calculated in the same way, but the comparison is made with someone of your age, gender, race, height, and weight.
In addition to bone densitometry testing, your doctor may recommend other types of tests, such as blood tests, which can be used to detect the presence of renal (kidney) disease, assess parathyroid function, assess the effect of cortisone therapy, and/or assess mineral levels in body related to bone strength, such as calcium.
Other related procedures that may be used to diagnose bone problems include bone scans and bone x-rays. Additional information can be found on the website or by phone. The list of services is presented below in the article.
What are the reasons for a bone density test?
A bone densitometry test is performed primarily to identify individuals with osteoporosis and low bone mass so that appropriate medical therapy and treatment can be administered. Early treatment helps prevent future bone fractures. It may also be recommended for individuals who have already had a fracture and are considered at risk for osteoporosis.
In patients with osteoporosis, the complications of broken bones are often severe, especially in the elderly. The earlier osteoporosis can be identified, the sooner effective treatment can be applied, which is more likely to reduce the severity of the condition.
You can also use bone densitometry testing:
- To confirm a diagnosis of osteoporosis if you already had a fracture
- Predict your chances of faults in the future
- To determine the velocity of bone mass loss and / or control the effects of treatment
- There may be other reasons why your doctor can recommend bone densitometry.
You can sign up for a consultation and find out in more detail from the administrator by phone +7 (495) 356-30-03.